Mybatis中setParameters分析
在使用MyBatis时,有两种使用方法。一种是使用的接口形式,另一种是通过SqlSession调用命名空间。这两种方式在传递参数时是不一样的,命名空间的方式更直接,但是多个参数时需要我们自己创建Map或者实体对象作为入参。
最近写东西发现了一个有意思的问题,以SqlSession方式在dao层我设定了接受参数类型为一个实体对象,可是传入map也可以成功解析。于是跟进看了一下源码,也在学习中,可能会出现问题,欢迎指出。
测试中我们定义了接受参数为一个Userinfo的实体类对象user,传入时使用map类型传入
在Mybatis 设置参数中
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = this.boundSql.getParameterMappings();
构造xml #{xxx}的mappings
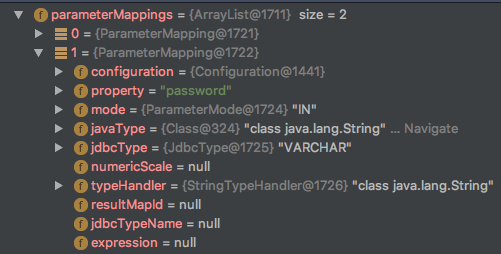
我们没有传入实体类对象而传入的map类型数据
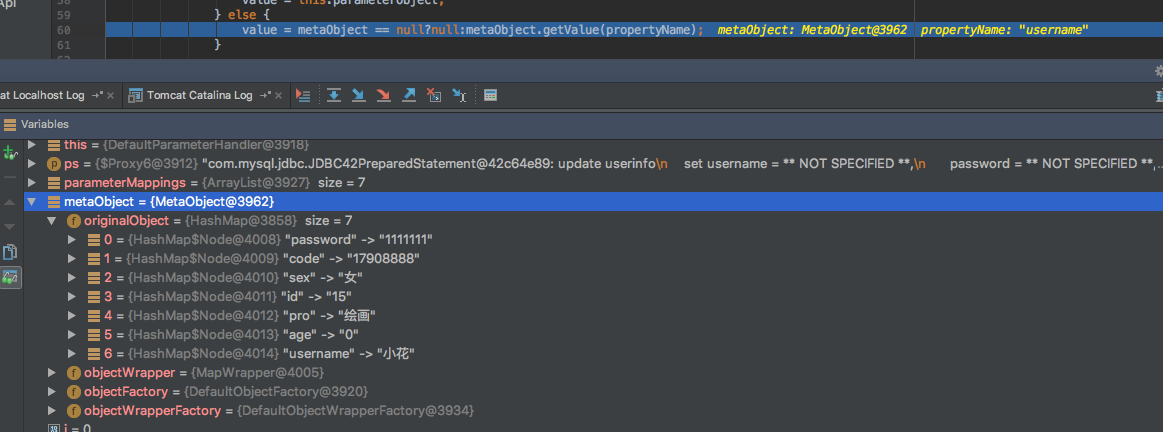
执行DefaultParameterHandler类中setParameters方法
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(this.mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = this.boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if(parameterMappings != null) {
MetaObject metaObject = this.parameterObject == null?null:this.configuration.newMetaObject(this.parameterObject);
for(int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); ++i) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)parameterMappings.get(i);
if(parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
Object value;
if(this.boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = this.boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if(this.parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if(this.typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(this.parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = this.parameterObject;
} else {
value = metaObject == null?null:metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if(value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = this.configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
}
}
}
}
其中
MetaObject metaObject = this.parameterObject == null?null:this.configuration.newMetaObject(this.parameterObject);
实例化MetaObject对象并且MetaObject类的构造方法判断了我们传入参数(user(map))的类型并指定objectWrapper的实现接口
MetaObject是MyBatis的一个反射类,可以很方便的通过getValue方法获取对象的各种属性(支持集合数组和Map,可以多级属性点.访问,如user.username,user.roles[1].rolename)。
private MetaObject(Object object, ObjectFactory objectFactory, ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory) {
this.originalObject = object;
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
this.objectWrapperFactory = objectWrapperFactory;
if(object instanceof ObjectWrapper) {
this.objectWrapper = (ObjectWrapper)object;
} else if(objectWrapperFactory.hasWrapperFor(object)) {
this.objectWrapper = objectWrapperFactory.getWrapperFor(this, object);
} else if(object instanceof Map) {
this.objectWrapper = new MapWrapper(this, (Map)object);
} else if(object instanceof Collection) {
this.objectWrapper = new CollectionWrapper(this, (Collection)object);
} else {
this.objectWrapper = new BeanWrapper(this, object);
}
}
我们接着看setParameters
会执行四个关键判断
if(this.boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName))
第一个if当使用<foreach>的时候,MyBatis会自动生成额外的动态参数,如果propertyName是动态参数,就会从动态参数中取值
else if(this.parameterObject == null)
第二个if,如果参数是null,不管属性名是什么,都会返回null。
if(this.typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(this.parameterObject.getClass()))
第三个if,如果参数是一个简单类型,或者是一个注册了typeHandler的对象类型,就会直接使用该参数作为返回值,和属性名无关
最后的else,这种情况下是复杂对象或者Map类型,通过反射方便的取值
value = metaObject == null?null:metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
这里传入我们需要找的属性名
进入metaObject调用getValue
这里使用this.objectWrapper.get(prop);
最终调用了MapWrapper的实现接口
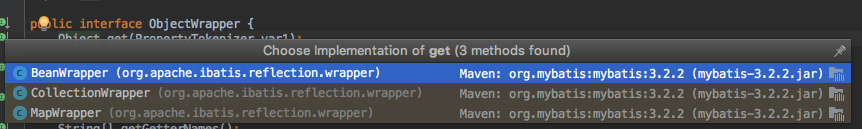
调用了MapWrapper下的get方法来获取map中value,其中BeanWrapper是获取传入实体的属性,他们同时都继承了BaseWrapper,之后的CollectionWrapper则会给你抛出异常告你错了,也就是说你传入的参数除了符合设定的类型,map和实体对象mybatis会加以判断 其他的如list如果不符合设置类型则会报UnsupportedOperationException异常。
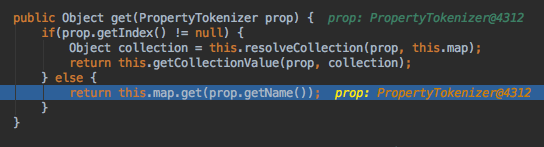
这样去找传入map中key与属性名称相同的value
举个例子更好理解mabitis处理参数类型方式
比如我的dao接口中定义了一个根据id查询用户的方法Userinfo selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id);并且用xml实现
我们在使用时可以
sqlSession = GetSqlSession.getSqlSession();
Userinfo user = (Userinfo) sqlSession.selectOne("cn.rui0.mapper.UserinfoMapper.selectByPrimaryKey", 1);
也可以用直接传对象或者map,自己设置的接收参数#{}会在给你解析map或对象后去匹配
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setId(1);
sqlSession = GetSqlSession.getSqlSession();
Userinfo user = (Userinfo) sqlSession.selectOne("cn.rui0.mapper.UserinfoMapper.selectByPrimaryKey", userinfo);
这样是可以成功请求的
但你用list就不行,即使你list里放个map

具体说 在set之前
mybatis把定义的xml#{xx}参数构造为mapping的形式(MappedStatement),我们知道SqlSource是一个接口类,在MappedStatement对象中是作为一个属性出现的,SqlSource接口只有一个getBoundSql(Object parameterObject)方法,返回一个BoundSql对象。而SqlSource最常用的实现类是DynamicSqlSource
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return boundSql;
}
调用DynamicContext,在DynamicContext类中,有对传入的parameterObject对象进行“map”化处理的部分,也就是说,你传入的pojo对象,会被当作一个键值对数据来源来进行处理,读取这个pojo对象的接口,还是Map对象。
具体可以看一下代码
public class DynamicContext {
public static final String PARAMETER_OBJECT_KEY = "_parameter";
public static final String DATABASE_ID_KEY = "_databaseId";
private final DynamicContext.ContextMap bindings;
private final StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
private int uniqueNumber = 0;
public DynamicContext(Configuration configuration, Object parameterObject) {
if(parameterObject != null && !(parameterObject instanceof Map)) {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
this.bindings = new DynamicContext.ContextMap(metaObject);
} else {
this.bindings = new DynamicContext.ContextMap((MetaObject)null);
}
this.bindings.put("_parameter", parameterObject);
this.bindings.put("_databaseId", configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
public Map<String, Object> getBindings() {
return this.bindings;
}
public void bind(String name, Object value) {
this.bindings.put(name, value);
}
public void appendSql(String sql) {
this.sqlBuilder.append(sql);
this.sqlBuilder.append(" ");
}
public String getSql() {
return this.sqlBuilder.toString().trim();
}
public int getUniqueNumber() {
return this.uniqueNumber++;
}
static {
OgnlRuntime.setPropertyAccessor(DynamicContext.ContextMap.class, new DynamicContext.ContextAccessor());
}
static class ContextAccessor implements PropertyAccessor {
ContextAccessor() {
}
public Object getProperty(Map context, Object target, Object name) throws OgnlException {
Map map = (Map)target;
Object result = map.get(name);
if(result != null) {
return result;
} else {
Object parameterObject = map.get("_parameter");
return parameterObject instanceof Map?((Map)parameterObject).get(name):null;
}
}
public void setProperty(Map context, Object target, Object name, Object value) throws OgnlException {
Map map = (Map)target;
map.put(name, value);
}
}
static class ContextMap extends HashMap<String, Object> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2977601501966151582L;
private MetaObject parameterMetaObject;
public ContextMap(MetaObject parameterMetaObject) {
this.parameterMetaObject = parameterMetaObject;
}
public Object get(Object key) {
String strKey = (String)key;
if(super.containsKey(strKey)) {
return super.get(strKey);
} else if(this.parameterMetaObject != null) {
Object object = this.parameterMetaObject.getValue(strKey);
if(object != null) {
super.put(strKey, object);
}
return object;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
}
在DynamicContext的构造函数中,可以看到,根据传入的参数对象是否为Map类型,有两个不同构造ContextMap的方式。而ContextMap作为一个继承了HashMap的对象,作用就是用于统一参数的访问方式:用Map接口方法来访问数据。
结束之后回到getBoundSql继续执行
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings()); BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
之后就会进行setParameters操作
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = this.boundSql.getParameterMappings();
从boundSql取出mapping

继续执行后续上面所说获取其中对象或map操作
总结一下,mybatis除了标准的设置传参类型的方式,也可以传入包含相同属性的对象或者key的map,同样也是可以执行的!
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/azengqiang/article/details/54377801
https://blog.csdn.net/isea533/article/details/44002219